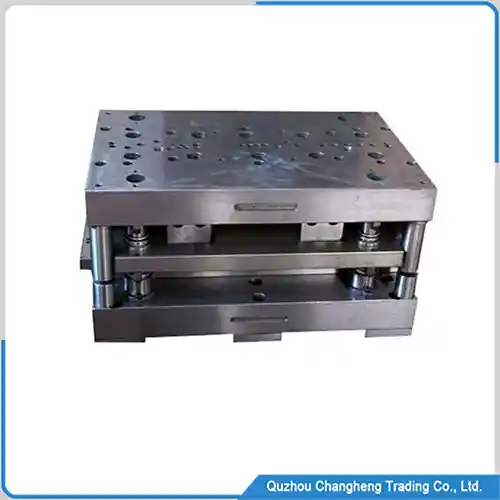
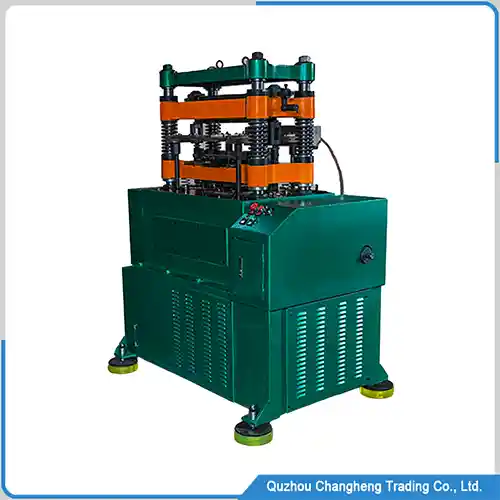




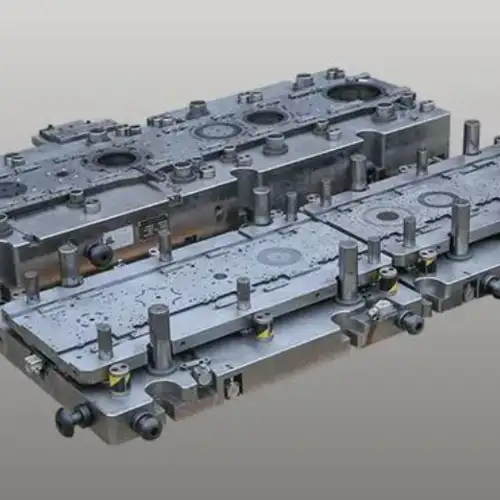
Mold Overview
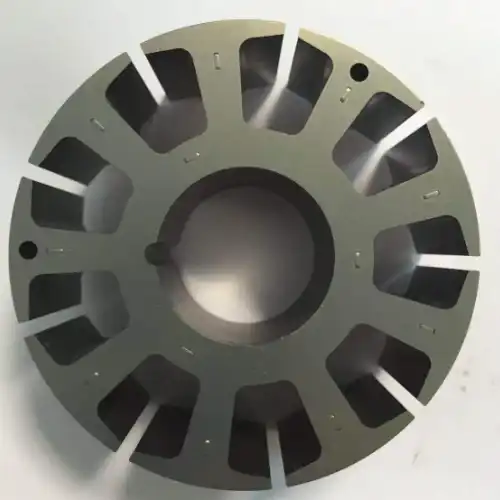
The motor stamping die is a laminated mold for producing motor iron cores. It has multiple mold cavities with different functions for cutting, punching, bending, etc. Continuous production is achieved through high-speed automatic stamping, which stacks iron sheets together to form the motor iron core.
There is a hollow channel at the bottom of the mold. The motor’s iron core automatically falls out of this channel when it reaches the specified height. The entire production process does not require workers’ participation; the iron core stamping mold automatically completes all the work.
Motor stamping die data
| No. | ITEM | DATA |
| 1 | Punching needle | SKH51 |
| 2 | Service life | 100 million times |
| 3 | Mold plate material | Cr12MoV |
| 4 | Appearance color | yellow |
| 5 | Rotor size | customized |
| 6 | Core height | freely controlled |
| 7 | Iron plate thickness | 0.1-2mm |
Motor stamping die advantage
- Fully automated production
Motor stamping molds and high-speed stamping machines can achieve fully automated production, improving production efficiency and reducing manufacturing costs.
- Long service life
The key components of this motor stamping mold are made of hard materials. They are treated with advanced vacuum quenching and tempering.
So, the mold has a long service life and can withstand long-term, large-scale stamping operations.
- No additional maintenance required
The motor stamping die does not require high maintenance costs when in use. Only a small amount of lubricating oil must be added to the guide column every month. It must be covered with a dust-proof cloth if it is not used for a long time.
- Low wear
Due to the very reasonable structural design of the mold, high-precision CNC machine tools process all parts, and all parts have undergone scientific and precise fit clearance. Its wear during use is relatively small and can maintain good precision output for a long time.
Motor stamping die main features
This stamping mold has various layout options, and the rotor and stator are produced in the same mold. This significantly improves production efficiency and reduces raw material waste, reducing production costs and increasing cost-effectiveness.
A new high-speed motor, whose coil channel adopts a rotating design. This design puts forward higher requirements for motor stamping die. Iron pieces need to rotate accurately during stacking; therefore, our stamping molds are equipped with servo motors at key positions to precisely control the iron core’s rotation angle to meet the iron core’s special requirements.
The shapes of the rotor and the stator are usually circular. To save materials, the motor stamping die has more than two geometric arrangements, which can save more than 20% of the raw materials. This layout design is suitable for factories that produce on a large scale, and it can save a lot of time and raw material costs every year.
Stamping die working video
Service and support
1. We accept stamping die designs and stator services for rotors and stators of any size.
2. I will find the best supplier in China if you only want to buy some iron cores for motors.
3. We offer a 12-month warranty policy or 5 million stamping cycles, during which we provide free repair services for any issues.
4. If your mold’s service life has expired, we can help you repair it and make it work again.
Why choose our molds
- Innovative technology:
CHANGHENG brand motor stamping die maintains innovative designs at the forefront of technology, providing the best solutions for the motor industry. Whether your motor is in the automotive, household, or electrical appliance industries, we can offer you the perfect solution.
- Competitive price:
Whether high-precision manufacturing technology or rich design experience, we always adhere to the people-oriented work concept. Saving money for customers is our driving force for working hard all the time.
- Redefine productivity:
Each part of our rotor mold is carefully designed, and key parts are precisely manufactured by CNC and treated by vacuum quenching. The mold adopts a multi-cavity layout. The rotor and stator are completed in one go, and we have made unremitting efforts to improve production efficiency.













 wechat
wechat